Understanding Metal Finishing Types Used In Metal Fabrication
When it comes to metal fabrication, the finishing process can be just as critical as the initial design and build. Metal finishes not only enhance the visual appeal of your project but also provide essential protective benefits.
In this article, FAB402 will go over the main types of metal finishes, as well as some lesser-used options, to give you a thorough understanding of your choices.
By understanding the different types of metal finishes and their benefits, our hope is that you can make informed decisions that meet your specific needs.
For more information or to discuss your next custom metal fabrication project, stop by the shop, give us a call, or request a quote online!
Popular Types of Metal Finishes
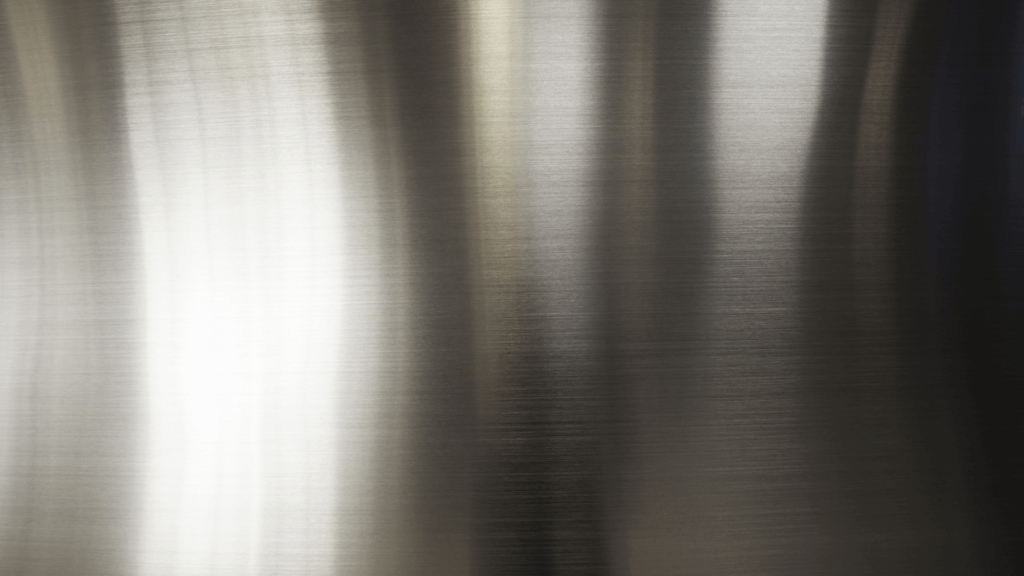

Polishing
What is it: Polishing is a process that smooths the surface of the metal to achieve a reflective, shiny finish.
What are the benefits: This finish is often used for decorative purposes. It enhances the appearance of the metal, making it look sleek and sophisticated. Polished metal is also easier to clean and maintain.

Brushing
What is it: Brushing gives the metal a satin finish by creating fine lines on the surface using abrasive belts or pads.
What are the benefits: This finish hides scratches and fingerprints better than polished metal, making it a popular choice for high-touch surfaces.
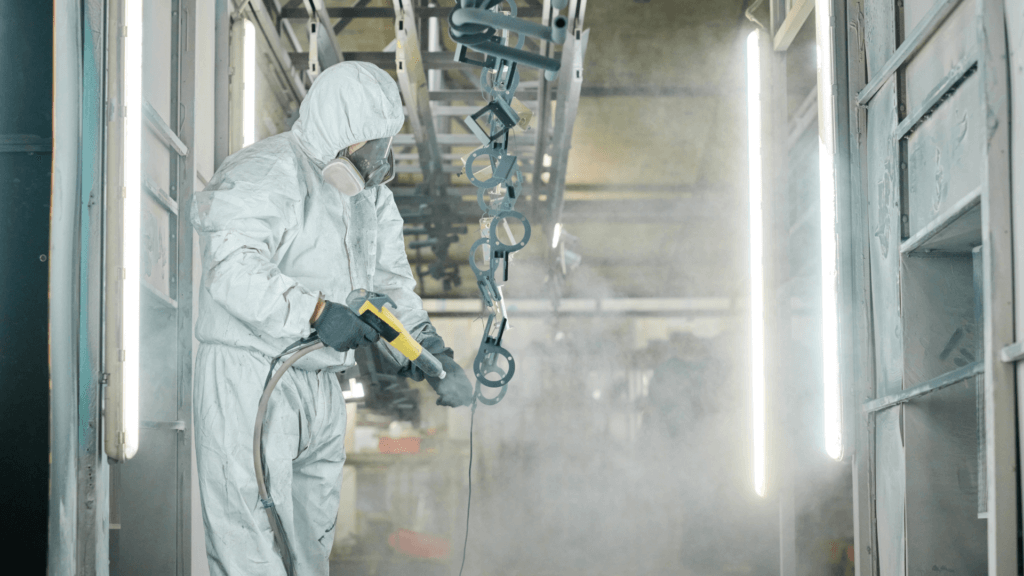

Powder Coating
What is it:Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the metal surface, which is then cured under heat to form a hard, durable finish.
What are the benefits: This finish offers superior durability, resistance to chipping, scratching, and fading. It also provides a wide range of color and texture options.
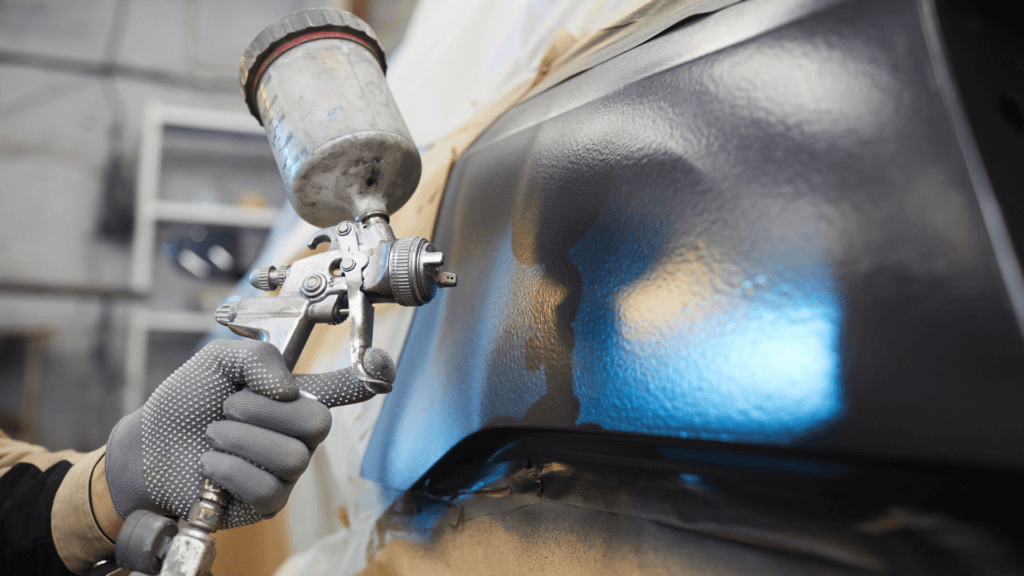
Painting
What is it:Painting involves applying liquid paint to the metal surface, followed by curing to achieve a smooth, colorful finish.
What are the benefits: This is a versatile finishing option that offers a wide range of colors and finishes, as well as additional protection against corrosion and wear.
Anodizing
What is it: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer.
What are the benefits: Anodized finishes are available in various colors and provide excellent protection against wear and corrosion.
Plating
What is it:Plating involves covering the metal surface with a thin layer of another metal, such as chrome, nickel, or gold.
What are the benefits: Plating enhances the appearance and provides additional corrosion resistance and wear protection.
Lesser-Used Metal Finishes
Blasting
What is it: Blasting involves propelling abrasive materials against the metal surface to clean and roughen it.
What are the benefits: This finish provides a uniform matte texture, improves paint adhesion, and removes surface contaminants.
Passivation
What is it: Passivation is a chemical process that removes free iron from the surface of stainless steel to enhance its corrosion resistance.
What are the benefits: This finish improves the metal’s resistance to rust and other forms of corrosion without changing its appearance.
Electropolishing
What is it: Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of metal to smooth and brighten the surface.
What are the benefits: This finish provides a high level of cleanliness, improved corrosion resistance, and a bright, reflective appearance.
Hot-Dip Galvanizing
What is it: Hot-dip galvanizing involves dipping the metal into molten zinc to form a protective coating.
What are the benefits: This finish provides excellent corrosion resistance, especially for outdoor and industrial applications.
Patina
What is it: Patina is a natural or chemically induced surface change that creates a weathered, antique look.
What are the benefits: This finish adds aesthetic appeal and uniqueness to the metal while providing some level of protection.
Chemical Conversion Coating
What is it: This process involves applying a chemical solution to the metal surface to form a protective oxide or phosphate layer.
What are the benefits: It enhances corrosion resistance and provides a good base for painting or other coatings.
Choosing the Right Metal Finish
When selecting a metal finish for your project, consider the following factors:
Functionality: Determine the primary purpose of the finish. Is it for aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, wear protection, or a combination of these factors?
Environment: Consider the environment in which the metal will be used. Outdoor and industrial applications may require more robust finishes like powder coating or hot-dip galvanizing.
Maintenance: Some finishes require more maintenance than others. Polished finishes, for example, may need regular cleaning to maintain their appearance.
Aesthetic Preferences: Choose a finish that aligns with the desired look and feel of your project. Brushed and patina finishes offer a more rustic appearance, while polished and plated finishes provide a sleek, modern look.
Cost: Budget constraints may influence your choice of finish. Some processes, like anodizing and electroplating, can be more expensive than painting or brushing.
