The Role of CAD & 3D Modeling
In Modern Metal Fabrication
The metal fabrication industry has witnessed a profound transformation over the past few decades, thanks to the emergence of computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling technologies. Gone are the days when fabricators relied solely on pencil, paper, and drafting tables to bring their ideas to life.
Today, cutting-edge software and advanced modeling techniques have revolutionized the way we approach design and fabrication, allowing for great improvement in precision, efficiency, and innovation.
In this article, FAB402 will explore the role of CAD and 3D modeling in modern metal fabrication, and look ahead to the future innovations that promise to further enhance our capabilities.
The Evolution from Pencil and Paper to CAD and 3D Modeling
The Traditional Approach
Before the rise of CAD and 3D modeling, metal fabrication was a labor-intensive process that required meticulous attention to detail. Draftsmen would spend hours, if not days, creating detailed blueprints by hand. Every line, curve, and dimension had to be manually calculated and drawn, leaving ample room for human error.
Revising these drawings was equally cumbersome, often requiring the entire blueprint to be redrawn. This traditional approach was not only time-consuming but also limited the complexity of designs that could be practically achieved.
The Shift to CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
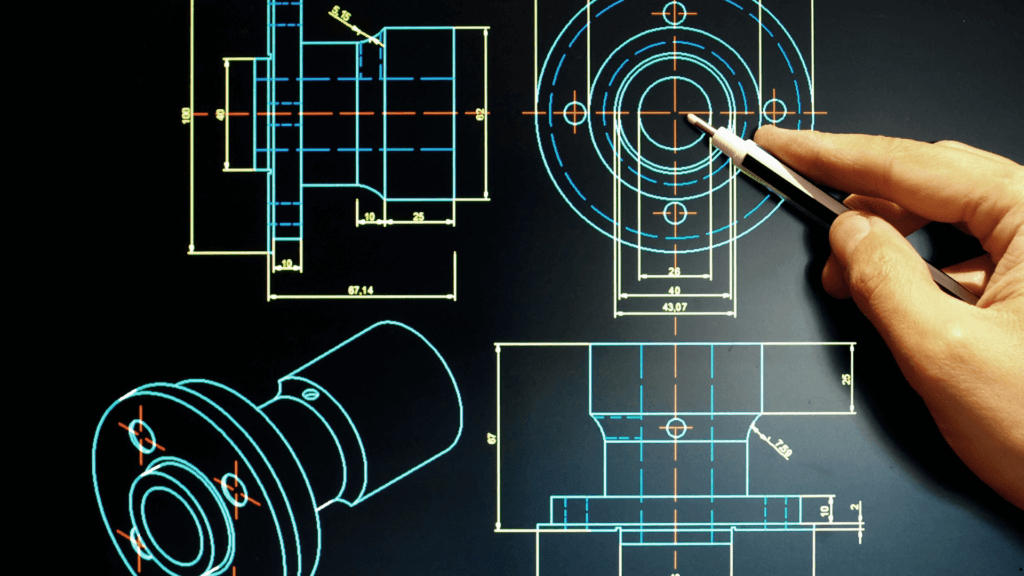
The introduction of CAD technology marked a significant turning point in the metal fabrication industry. CAD software allows designers to create precise digital representations of their projects. These digital blueprints can be easily modified, shared, and stored, eliminating the need for physical storage space and reducing the risk of damage or loss.
CAD software offers numerous advantages over traditional methods:
Precision and Accuracy: CAD software ensures that designs are highly accurate, down to the smallest detail. This precision translates to better-fitting parts and assemblies, reducing waste and rework.
Efficiency: With CAD, designers can quickly create and modify designs, significantly speeding up the design process. This efficiency allows for faster project turnaround times and the ability to take on more projects.
Complexity: CAD enables the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be nearly impossible to achieve with pencil and paper. This capability has opened up new possibilities in metal fabrication, allowing for more innovative and sophisticated projects.
The Emergence of 3D Modeling
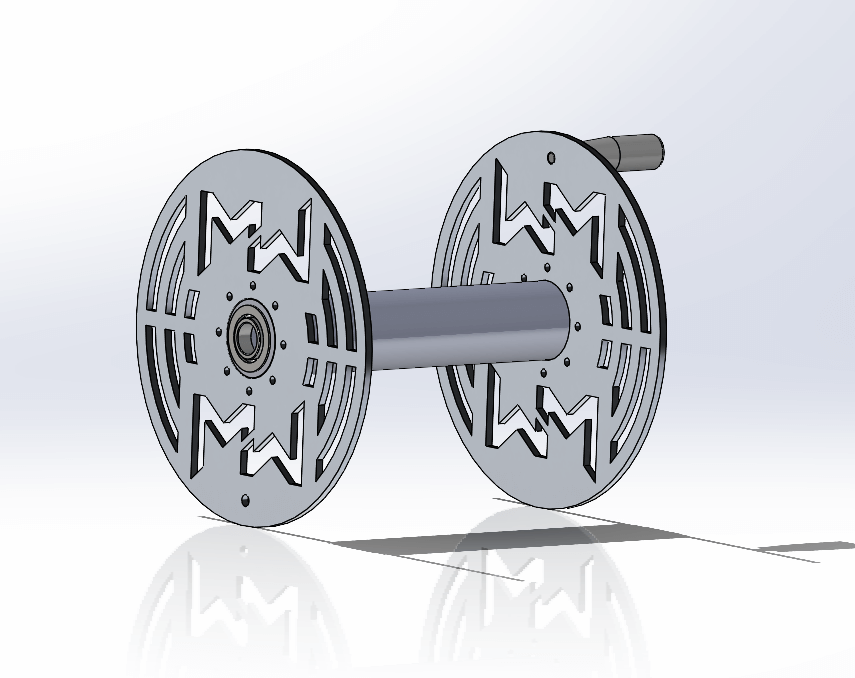
Building on the foundation of CAD, 3D modeling has further revolutionized metal fabrication. While CAD provides detailed 2D blueprints, 3D modeling offers fully-rendered, realistic representations of the final product. This technology allows designers and clients to visualize the project from every angle, ensuring that the design meets their expectations before fabrication begins.
3D modeling offers several key benefits:
Visualization: 3D models provide a clear, realistic view of the final product, making it easier for clients to understand and approve the design. This visualization helps bridge the gap between concept and reality.
Simulation and Testing: 3D modeling software often includes simulation tools that allow designers to test the structural integrity and functionality of the design under various conditions. This capability helps identify potential issues early in the design process, reducing the risk of costly errors during fabrication.
Customization: 3D modeling makes it easier to customize designs to meet specific client requirements. Designers can quickly adjust dimensions, shapes, and features to create tailored solutions for each project.
The Future of CAD and 3D Modeling in Metal Fabrication
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are ready to revolutionize CAD and 3D modeling. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and optimize designs for performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
AI-powered design tools can also automate routine tasks, allowing designers to focus on more creative and strategic aspects of their work.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are set to transform the way we interact with 3D models. With AR, designers and clients can overlay digital models onto the physical world, providing a more immersive and interactive experience. VR, on the other hand, allows for virtual walkthroughs and inspections of the design, making it possible to explore the project in a fully immersive environment.
Cloud-Based Collaboration
Cloud-based CAD and 3D modeling platforms are making it easier for teams to collaborate on projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location. These platforms enable seamless sharing of designs, instant feedback, and collaborative problem-solving, enhancing productivity and allowing everyone to be on the same page.
Advanced Simulation and Analysis
Future advancements in simulation and analysis tools will provide even more detailed insights into the performance of designs. These tools will be able to simulate a wider range of conditions and scenarios, helping to identify potential issues and optimize designs for durability, safety, and efficiency.
